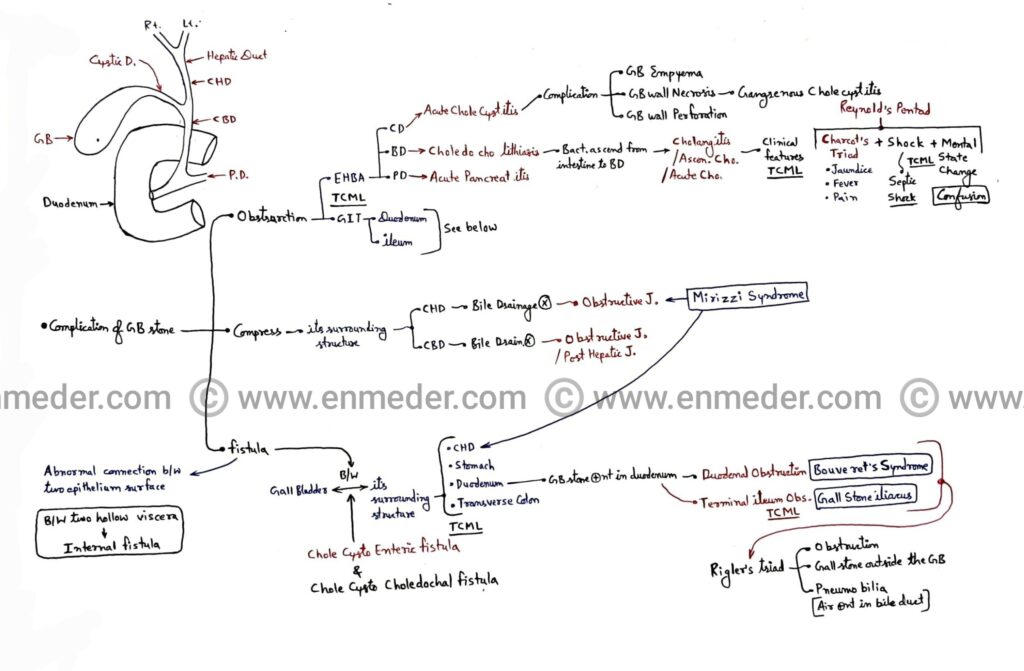
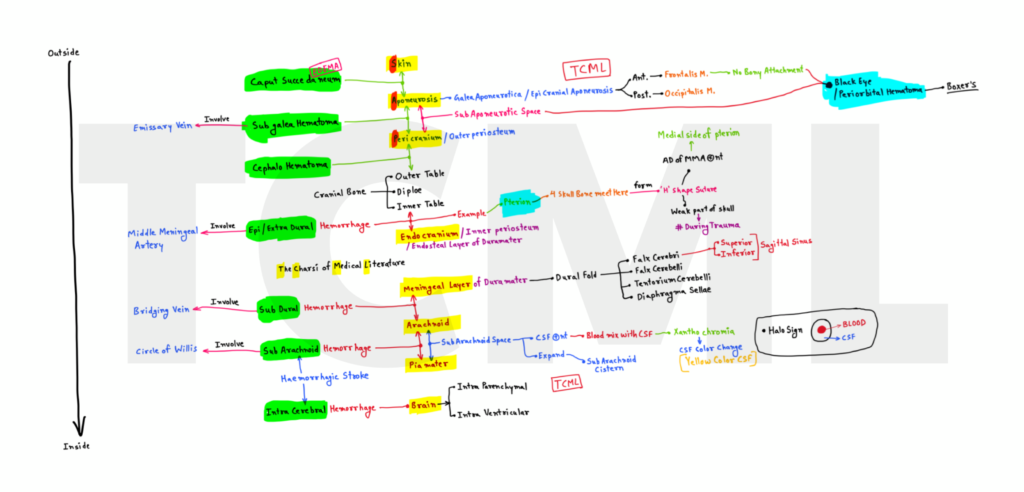
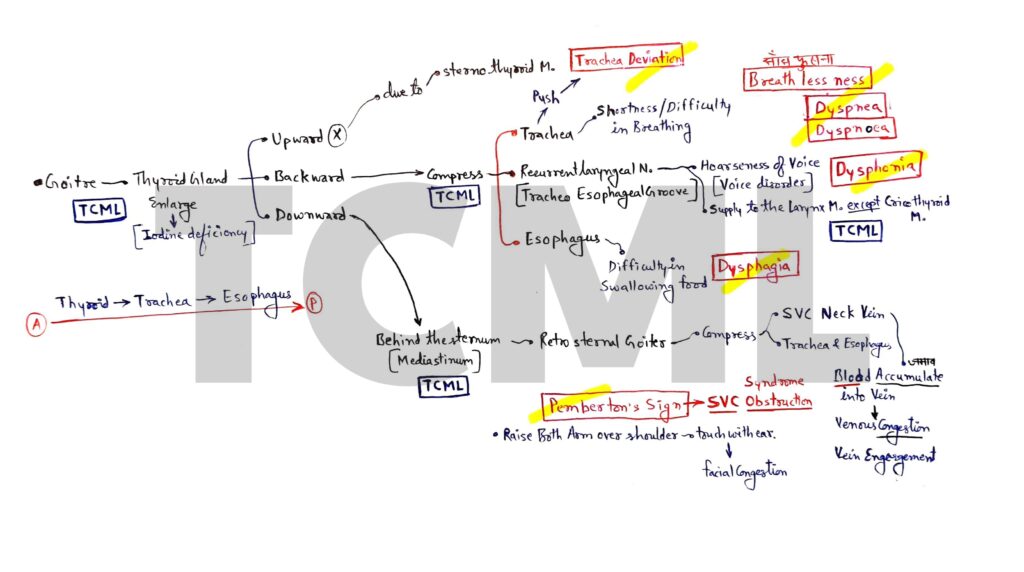
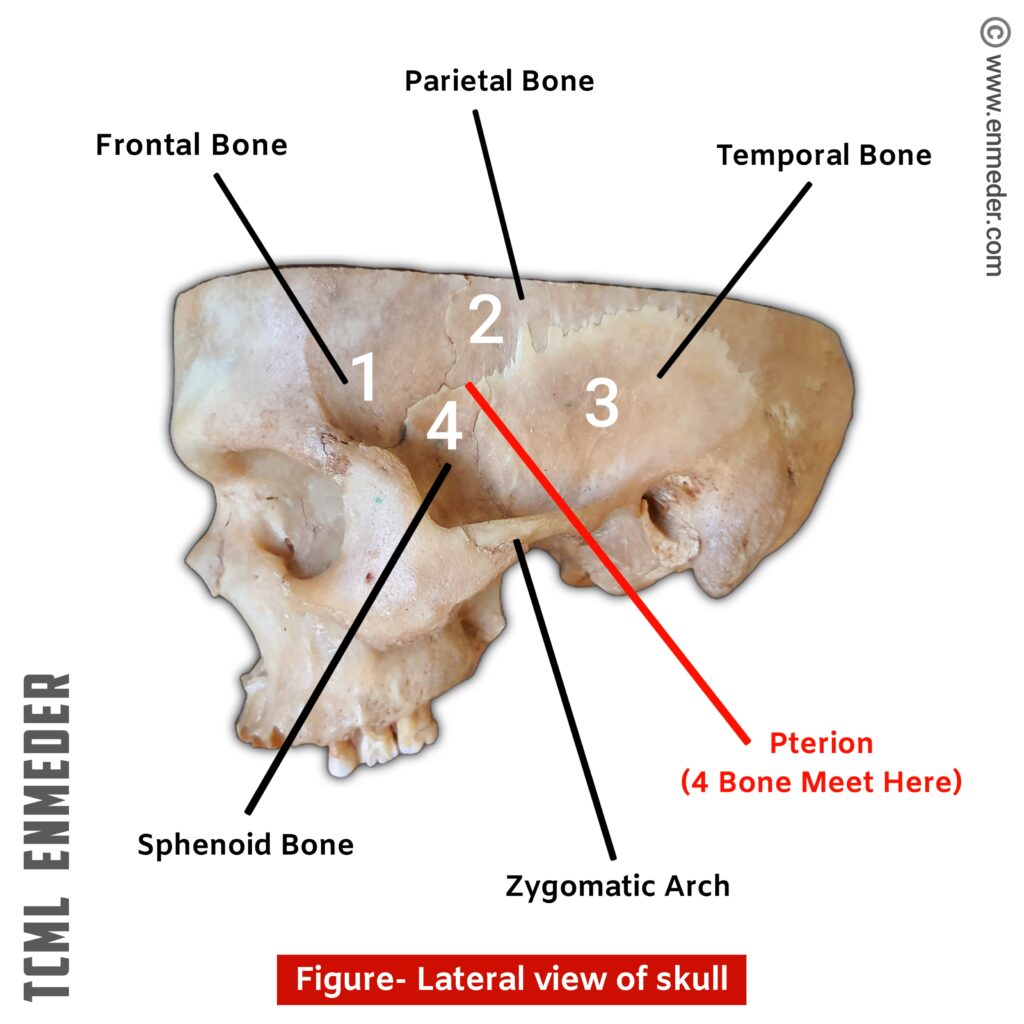
GallBladder stone
Complications of gallstone/cholelithiasis- 1. Obstruction of extra hepatic biliary apparatus and gastrointestinal tract 2. Compression of common hepatic duct and common bile duct 3. Fistula between gallbladder and it’s surrounding structures 1. Obstruction – A. Extra hepatic biliary apparatus (EHBA) – 1. Cystic duct (CD)Due to obstruction of cystic duct by gallstone it causes acute […]